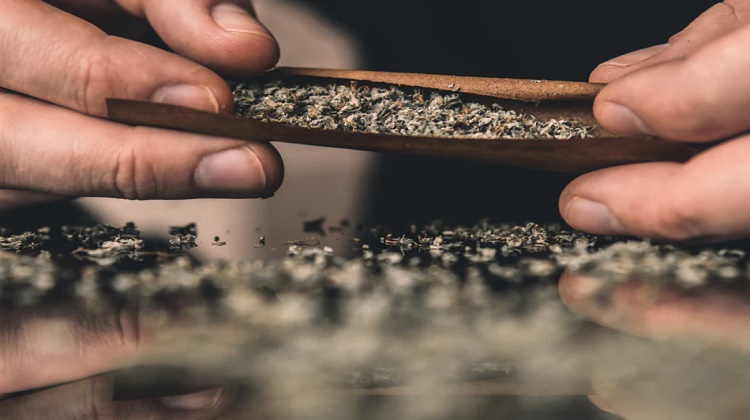
When it comes to cannabis, most people are familiar with THC, the psychoactive compound that produces euphoric effects. However, there is an often-overlooked compound that many believe to have therapeutic potential: THCA. THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is the non-psychoactive precursor to THC that naturally occurs in the cannabis plant. In this blog post, we will delve into what THCA is and its therapeutic potential.
THCA is a cannabinoid that is abundant in raw, fresh cannabis. Unlike THC, THCA is non-psychoactive, meaning that it doesn’t produce the typical “high” associated with cannabis. When cannabis is heated, THCA is converted to THC through a process known as decarboxylation. The heat causes the carboxylic acid group to break off, turning THCA to THC.
While THCA itself doesn’t produce intoxicating effects, there is a growing body of research suggesting that it has potential therapeutic benefits. A study published in the Journal of Natural Products found that THCA had anti-inflammatory properties, which may make it an effective treatment for conditions associated with inflammation, such as arthritis and multiple sclerosis. Additionally, THCA has been found to have neuroprotective properties, which may make it a useful treatment for neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Another potential use for THCA is as an antiemetic, or a medication that helps to relieve nausea and vomiting. A study published in the British Journal of Pharmacology found that THCA reduced vomiting in rats, suggesting that it may be a useful treatment for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.
THCA may also be useful for treating pain. A study conducted by the University of Guelph found that THCA reduced pain and inflammation in mice. While more research is needed to determine if these effects translate to humans, this suggests that THCA may be a useful treatment for chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain.
In addition to its therapeutic potential, THCA has several other benefits. For one, it may be more accessible than THC for patients who don’t want to experience psychoactive effects. Additionally, THCA is more stable than THC, meaning that it doesn’t degrade as quickly and has a longer shelf life. This makes it a useful medication for patients who require cannabis for medicinal purposes over an extended period.
Conclusion:
While more research is needed to fully understand the therapeutic potential of THCA, the initial findings are promising. THCA may be an effective treatment for inflammation, nausea, pain, and neurological conditions. It may also be more accessible than THC and has a longer shelf life. As always, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any new medication or treatment, including those involving THCA.